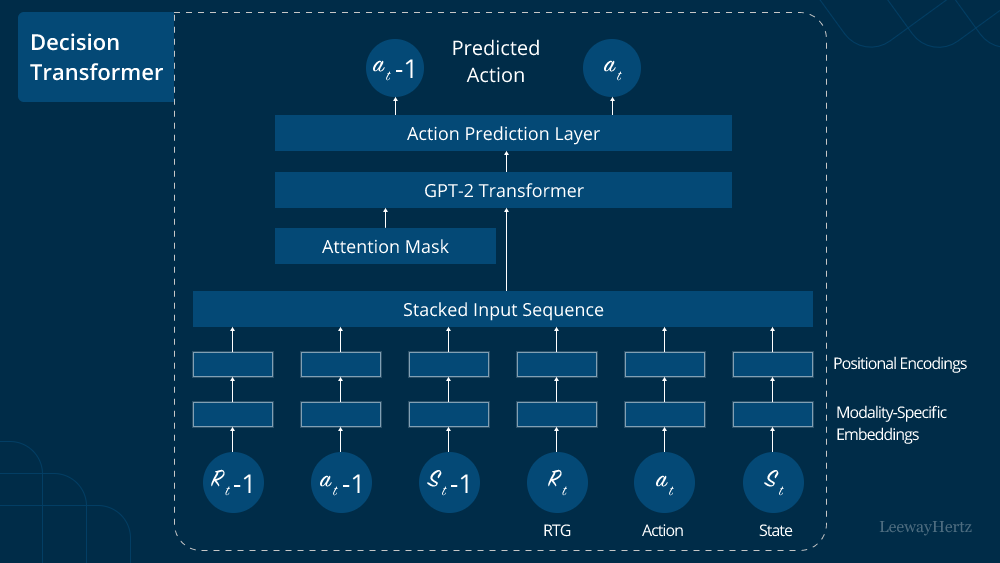
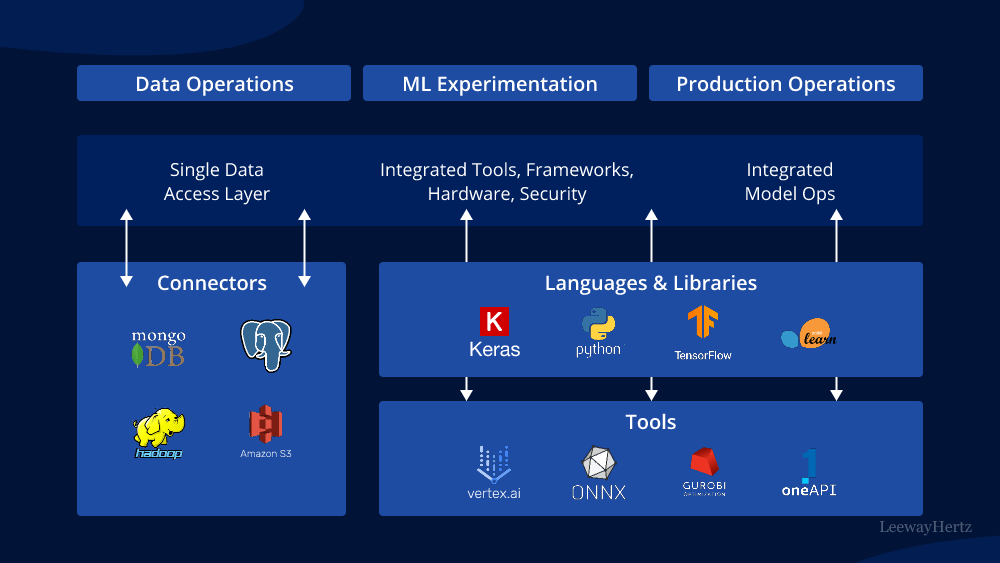
In recent years, the telecom industry has witnessed a remarkable transformation, thanks in large part to advancements in artificial intelligence (AI). One of the most exciting developments in this field is the integration of generative AI, which has opened up a plethora of opportunities and use cases for telecom companies. In this article, we will delve into the world of generative AI and explore its various applications within the telecom sector.
Understanding Generative AI
Generative AI is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on the creation of data, content, or even entire systems that resemble human-generated content. Unlike traditional AI, which relies on rule-based algorithms, generative AI leverages deep learning techniques, particularly neural networks, to generate novel content.
One of the most popular applications of generative AI is the generation of text, images, and even audio. These AI models, such as GPT-3, have demonstrated remarkable abilities in generating human-like text, making them invaluable tools for various industries, including telecom.
Use Cases of Generative AI in Telecom
The telecom industry is a vast and complex ecosystem that encompasses various domains, from network optimization to customer service. Generative AI has found its place in several facets of the telecom sector, and here are some prominent use cases:
1. Network Optimization
Telecom companies rely heavily on network infrastructure to deliver services to their customers. Ensuring optimal network performance and efficiency is paramount. Generative AI can be employed to simulate network conditions, predict potential issues, and recommend optimization strategies.
Using generative AI models, telecom engineers can create synthetic network data that closely resembles real-world scenarios. This data can then be used to test new network configurations and identify vulnerabilities, ultimately leading to more robust and reliable networks.
2. Predictive Maintenance
The maintenance of telecom equipment, such as cell towers and data centers, is a costly and crucial aspect of the industry. Generative AI can play a pivotal role in predictive maintenance by analyzing historical data and generating predictive models.
By forecasting when equipment is likely to fail or require maintenance, telecom companies can schedule repairs and replacements proactively, minimizing downtime and reducing operational costs.
3. Natural Language Processing for Customer Support
Customer support is a critical component of the telecom industry. Generative AI models equipped with natural language processing capabilities can be used to automate responses to customer queries and issues.
Chatbots and virtual assistants powered by generative AI can engage with customers in real-time, answer frequently asked questions, and even assist with troubleshooting common problems. This not only enhances the customer experience but also reduces the workload on human customer support agents.
4. Content Generation for Marketing
Telecom companies invest heavily in marketing and advertising to attract and retain customers. Generative AI can assist in content generation by creating compelling marketing copy, blog posts, and social media updates.
These AI-generated materials can be customized to target specific customer segments, ensuring that the content resonates with the intended audience and drives engagement.
5. Fraud Detection and Security
Security threats, including fraud and cyberattacks, pose a significant risk to telecom operators. Generative AI can be applied to identify patterns indicative of fraudulent activities.
By analyzing vast amounts of data, generative AI models can flag suspicious transactions and activities in real-time, helping telecom companies take immediate action to mitigate security risks and protect their customers’ data.
Challenges and Considerations
While generative AI holds great promise for the telecom industry, it is not without its challenges and considerations. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
1. Data Privacy and Ethics
Generative AI models require large datasets to train effectively. Telecom companies must ensure that the data used for training and inference adhere to strict privacy regulations and ethical standards. Protecting customer data is paramount.
2. Model Bias
Generative AI models can inherit biases present in their training data. Telecom companies must carefully curate their training datasets and implement measures to mitigate bias, ensuring fair and equitable outcomes.
3. Scalability
Implementing generative AI solutions at scale can be complex. Telecom companies need to invest in robust infrastructure and talent capable of developing, deploying, and maintaining these AI systems.
4. Integration with Existing Systems
Integrating generative AI into existing telecom systems and workflows can be challenging. Ensuring seamless compatibility and minimal disruption is crucial for successful adoption.
The Future of Generative AI in Telecom
As generative AI continues to evolve, its impact on the telecom industry is poised to grow. From optimizing networks to enhancing customer service and improving security, the applications of generative AI are vast and transformative.
Telecom companies that embrace generative AI and navigate its challenges effectively will be well-positioned to stay competitive and provide cutting-edge services to their customers. With the potential to revolutionize network management, customer engagement, and beyond, generative AI is undoubtedly a game-changer for the telecom industry.
In conclusion, a remarkable advancement of generative AI in the telecom industry, offering innovative solutions to age-old challenges. By harnessing the power of AI-driven content generation, predictive maintenance, and network optimization, telecom companies can not only improve operational efficiency but also deliver enhanced services and experiences to their customers. As technology continues to evolve, it is essential for telecom companies to stay at the forefront of these developments to remain competitive and meet the ever-growing demands of the modern digital age.